R Software in Criminological Research: Benefits of an Open Source Framework
Réka Solymosi
Department of Criminology
University of Manchester
reka.solymosi@manchester.ac.uk
![]()
Overview
- Brief introduction to the importance of data analysis in criminology
Overview
Brief introduction to the importance of data analysis in criminology
Overview of R as an open-source programming language and software environment
Overview
Brief introduction to the importance of data analysis in criminology
Overview of R as an open-source programming language and software environment
Advantages of R
Overview
Brief introduction to the importance of data analysis in criminology
Overview of R as an open-source programming language and software environment
Advantages of R
Examples of utility
Overview
Brief introduction to the importance of data analysis in criminology
Overview of R as an open-source programming language and software environment
Advantages of R
Examples of utility
How to get started
Overview
Brief introduction to the importance of data analysis in criminology
Overview of R as an open-source programming language and software environment
Advantages of R
Examples of utility
How to get started
Practice example
Overview
Brief introduction to the importance of data analysis in criminology
Overview of R as an open-source programming language and software environment
Advantages of R
Examples of utility
How to get started
Practice example
Q & A
The importance of data analysis in criminology
The importance of data analysis in criminology
- Academic Research and Theoretical Development
The importance of data analysis in criminology
Academic Research and Theoretical Development
Understanding Crime Patterns
The importance of data analysis in criminology
Academic Research and Theoretical Development
Understanding Crime Patterns
Informed Decision-Making
The importance of data analysis in criminology
Academic Research and Theoretical Development
Understanding Crime Patterns
Informed Decision-Making
Evaluation of Criminal Justice Policies
The importance of data analysis in criminology
Academic Research and Theoretical Development
Understanding Crime Patterns
Informed Decision-Making
Evaluation of Criminal Justice Policies
Interdisciplinary Applications
The importance of data analysis in criminology
Academic Research and Theoretical Development
Understanding Crime Patterns
Informed Decision-Making
Evaluation of Criminal Justice Policies
Interdisciplinary Applications
and so on...
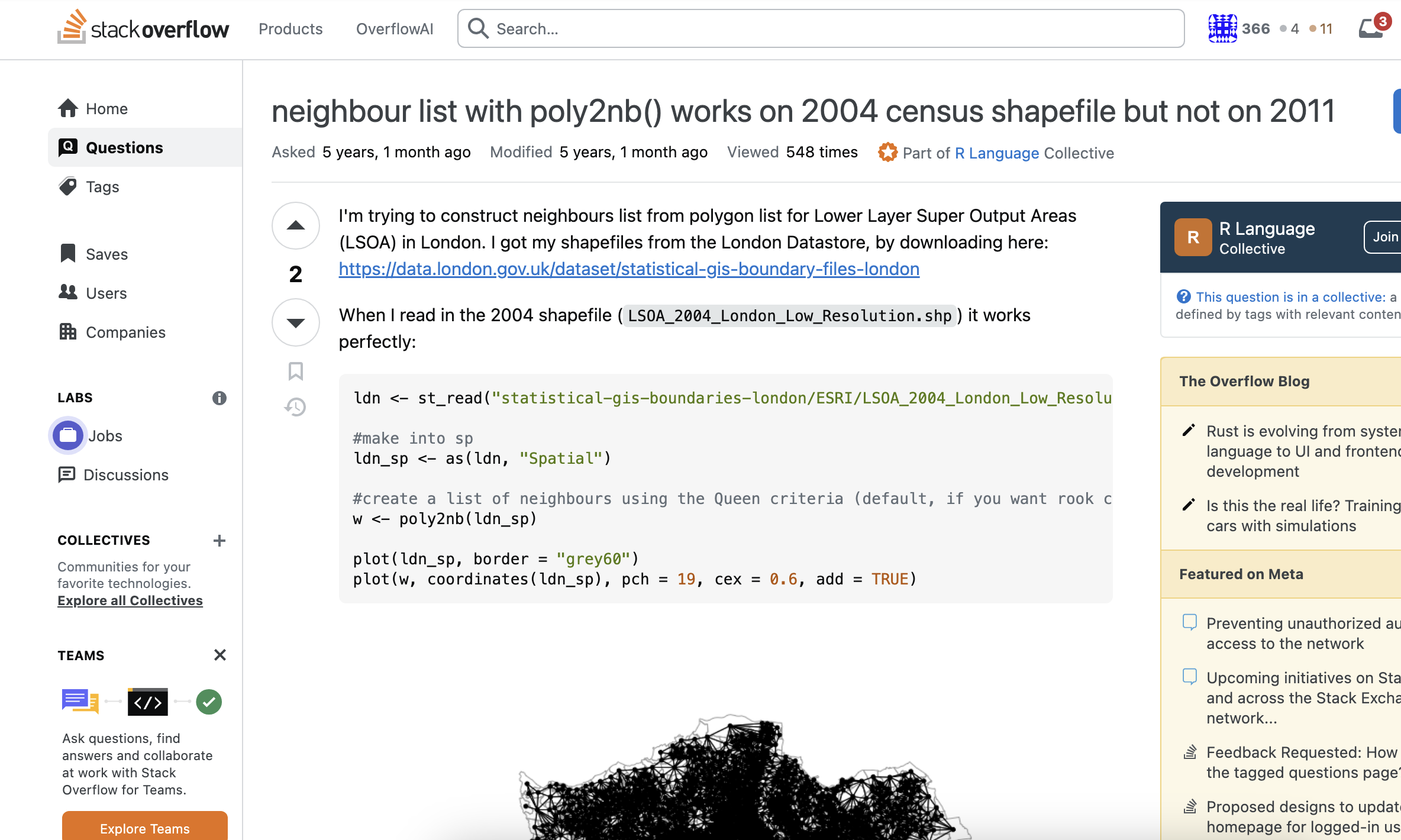
So why R?
Reason 1: Open source
Free (accessible)
- For students, teachers, professionals
- No licence required
- Download R: https://www.r-project.org/
- Download R Studio (IDE): https://posit.co/downloads/
Many contributors (range of packages)
- Any type of analysis you want to do - it is possible
- Anyone can contribute
- If it doesn't exist, someone will write it

Community support
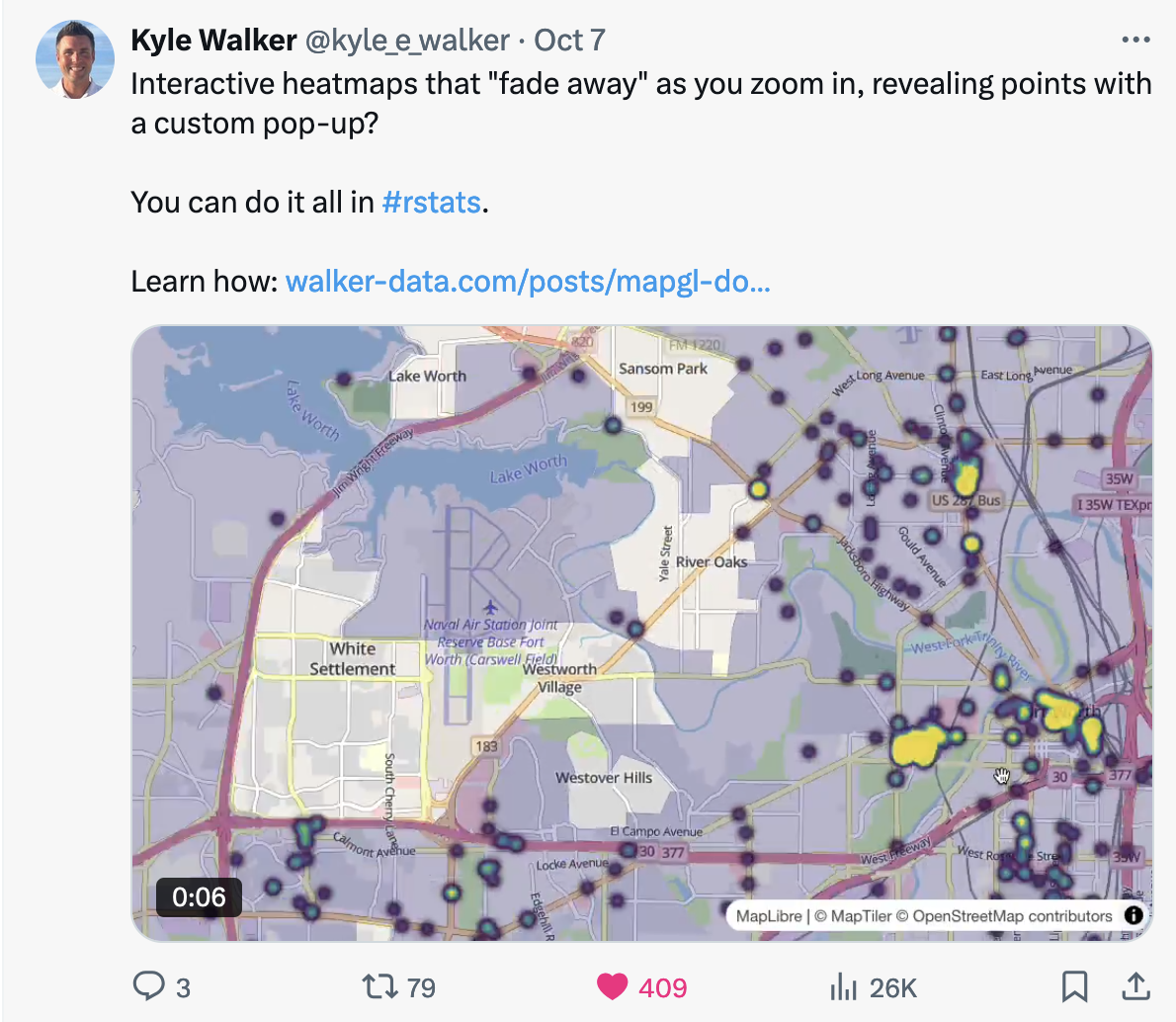
Community support
Community support
Community support
Reason 2: Versatile
Data
library(fivethirtyeight)head(hate_crimes)## state state_abbrev median_house_inc share_unemp_seas share_pop_metro## 1 Alabama AL 42278 0.060 0.64## 2 Alaska AK 67629 0.064 0.63## 3 Arizona AZ 49254 0.063 0.90## 4 Arkansas AR 44922 0.052 0.69## 5 California CA 60487 0.059 0.97## 6 Colorado CO 60940 0.040 0.80## share_pop_hs share_non_citizen share_white_poverty gini_index share_non_white## 1 0.821 0.02 0.12 0.472 0.35## 2 0.914 0.04 0.06 0.422 0.42## 3 0.842 0.10 0.09 0.455 0.49## 4 0.824 0.04 0.12 0.458 0.26## 5 0.806 0.13 0.09 0.471 0.61## 6 0.893 0.06 0.07 0.457 0.31## share_vote_trump hate_crimes_per_100k_splc avg_hatecrimes_per_100k_fbi## 1 0.63 0.12583893 1.8064105## 2 0.53 0.14374012 1.6567001## 3 0.50 0.22531995 3.4139280## 4 0.60 0.06906077 0.8692089## 5 0.33 0.25580536 2.3979859## 6 0.44 0.39052330 2.8046888Analysis
library(skimr)skim(hate_crimes)| skim_variable | n_missing | numeric.mean | numeric.hist |
|---|---|---|---|
| state | 0 | NA | NA |
| median_house_inc | 0 | 5.522361e+04 | ▂▆▇▅▂ |
| share_unemp_seas | 0 | 4.956860e-02 | ▅▇▇▇▂ |
| share_pop_metro | 0 | 7.501961e-01 | ▁▂▅▆▇ |
| share_pop_hs | 0 | 8.691176e-01 | ▃▅▃▆▇ |
| share_non_citizen | 3 | 5.458330e-02 | ▇▆▆▂▂ |
Summary stats
summary_hate_crimes <- summary(hate_crimes$hate_crimes_per_100k_splc)summary_hate_crimes## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. NA's ## 0.06745 0.14271 0.22620 0.30409 0.35694 1.52230 4T-test
# Create a new variable to categorise stateshate_crimes$income_category <- ifelse(hate_crimes$median_house_inc > median(hate_crimes$median_house_inc), "High", "Low")# Perform a t-testt_test_result <- t.test(hate_crimes$hate_crimes_per_100k_splc ~ hate_crimes$income_category)t_test_result## ## Welch Two Sample t-test## ## data: hate_crimes$hate_crimes_per_100k_splc by hate_crimes$income_category## t = 2.1658, df = 27.187, p-value = 0.03926## alternative hypothesis: true difference in means between group High and group Low is not equal to 0## 95 percent confidence interval:## 0.008498125 0.312551012## sample estimates:## mean in group High mean in group Low ## 0.3894784 0.2289538Missing values
missing_values <- sum(is.na(hate_crimes$hate_crimes_per_100k_splc))missing_values## [1] 4Calculate correlation
correlation <- cor.test(hate_crimes$median_house_inc, hate_crimes$hate_crimes_per_100k_splc, use = "complete.obs", method = "pearson")correlation## ## Pearson's product-moment correlation## ## data: hate_crimes$median_house_inc and hate_crimes$hate_crimes_per_100k_splc## t = 2.5122, df = 45, p-value = 0.01565## alternative hypothesis: true correlation is not equal to 0## 95 percent confidence interval:## 0.07066435 0.57951602## sample estimates:## cor ## 0.3507143Calculate regression
# Fit a linear regression modelmodel <- lm(hate_crimes_per_100k_splc ~ median_house_inc + share_vote_trump + share_non_citizen, data = hate_crimes)summary(model)## ## Call:## lm(formula = hate_crimes_per_100k_splc ~ median_house_inc + share_vote_trump + ## share_non_citizen, data = hate_crimes)## ## Residuals:## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max ## -0.35450 -0.11333 -0.04116 0.08900 0.50329 ## ## Coefficients:## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|) ## (Intercept) 1.626e+00 3.996e-01 4.068 0.00021 ***## median_house_inc -4.351e-06 4.122e-06 -1.056 0.29729 ## share_vote_trump -2.006e+00 3.880e-01 -5.169 6.5e-06 ***## share_non_citizen -2.083e+00 1.149e+00 -1.814 0.07707 . ## ---## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1## ## Residual standard error: 0.1881 on 41 degrees of freedom## (6 observations deleted due to missingness)## Multiple R-squared: 0.4791, Adjusted R-squared: 0.441 ## F-statistic: 12.57 on 3 and 41 DF, p-value: 5.751e-06Present results nicely
library(broom)# Tidy the model resultstidy_model <- tidy(model)# Print the tidy model as an HTML tabletidy_model %>% knitr::kable("html", caption = "Regression Results") %>% kableExtra::kable_styling(full_width = FALSE)| term | estimate | std.error | statistic | p.value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 1.6255048 | 0.3996144 | 4.067683 | 0.0002104 |
| median_house_inc | -0.0000044 | 0.0000041 | -1.055686 | 0.2972927 |
| share_vote_trump | -2.0056482 | 0.3879999 | -5.169197 | 0.0000065 |
| share_non_citizen | -2.0833768 | 1.1487938 | -1.813534 | 0.0770737 |
library(sjPlot)# Create a forest plot for the regression modelplot_model(model, type = "est", show.values = TRUE, show.ci = TRUE) + labs(title = "Forest Plot of Regression Coefficients", x = "Estimate", y = "Predictors")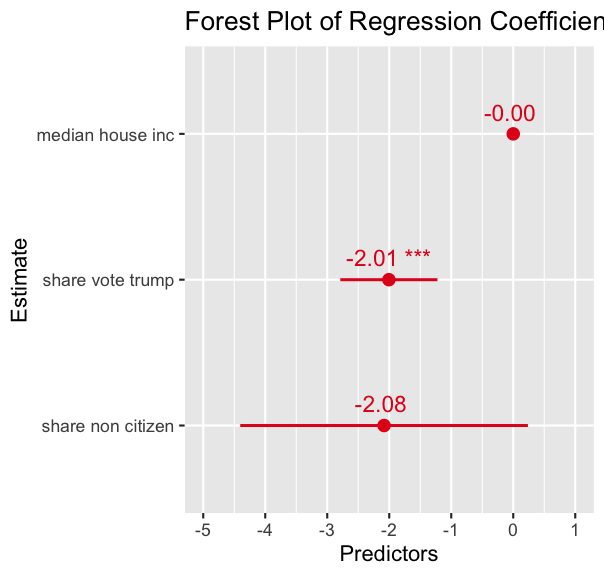
Many types of analysis
Network
# Load the librarieslibrary(igraph)library(igraphdata)# Load a sample network datasetdata("USairports")# Plot the network graphplot(USairports, vertex.size=5, vertex.label=NA, edge.arrow.size=0.3, main="US Airports Network")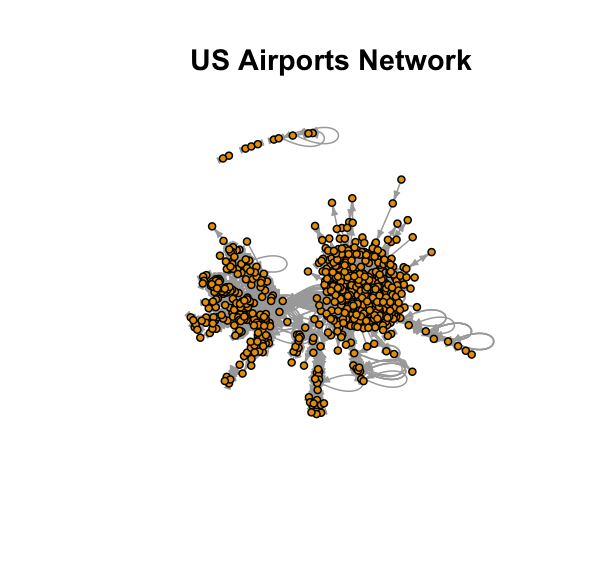
Spatial
# Load the librarylibrary(tmap)# Load the inbuilt datasetdata("World")# Create a quick maptm_shape(World) + tm_polygons("pop_est", title = "Population") + tm_layout(main.title = "World Population Map", frame = FALSE)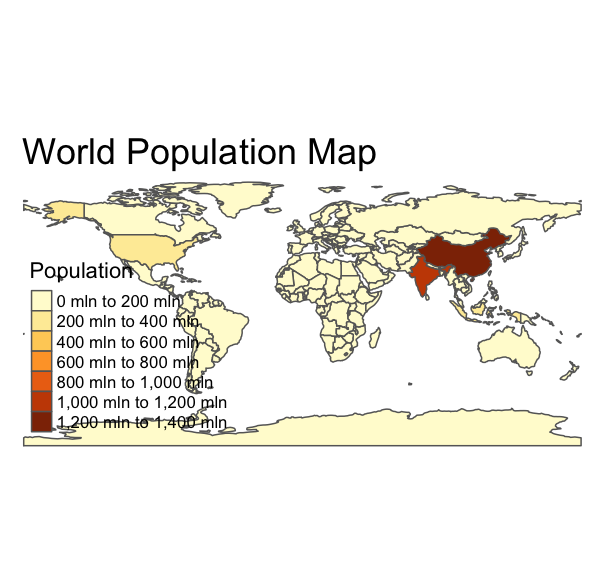
Text
# Load the librarieslibrary(wordcloud)library(tm)# Load a sample text datasetdata("crude")# Create a term-document matrixtdm <- TermDocumentMatrix(crude)# Convert the matrix to a format for word cloudm <- as.matrix(tdm)word_freq <- sort(rowSums(m), decreasing=TRUE)# Generate the word cloudwordcloud(names(word_freq), word_freq, max.words=100)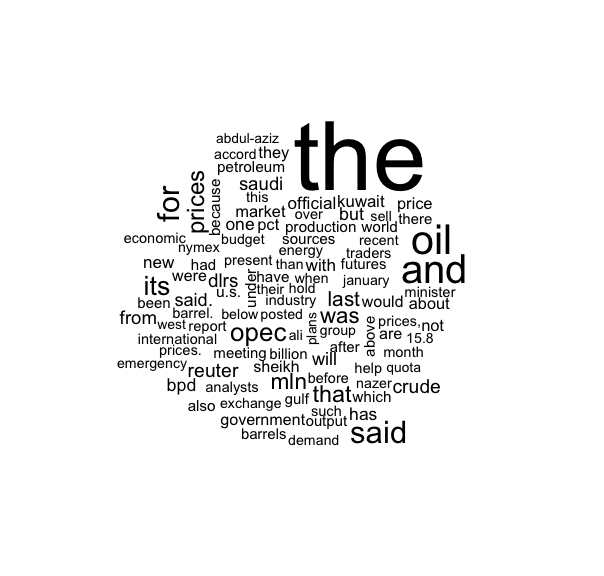
Machine learning
# Load the librarieslibrary(rpart)library(ggparty)# Load the datasetdata(iris)# Create a decision tree model using rpart directlymodel <- rpart(Species ~ ., data = iris)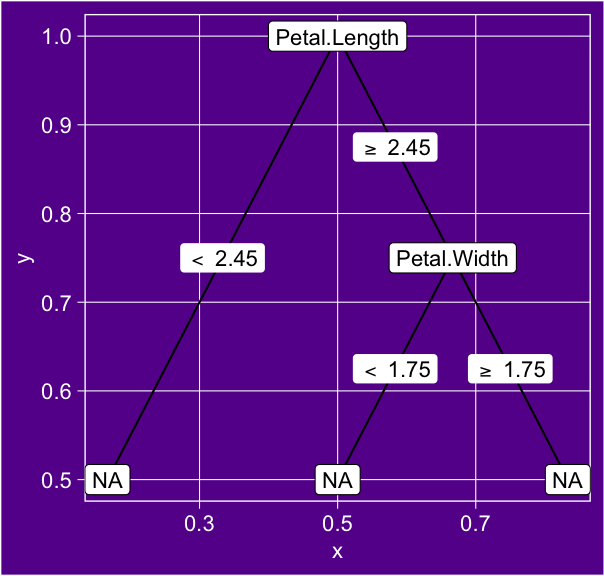
More ML
library(caret)# Load the iris datasetdata(iris)# Split the data into training and testing sets (70% training, 30% testing)set.seed(123)trainIndex <- createDataPartition(iris$Species, p = 0.7, list = FALSE)trainData <- iris[trainIndex, ]testData <- iris[-trainIndex, ]# Train a KNN modelmodel <- train(Species ~ ., data = trainData, method = "knn", tuneLength = 5)# Predict on the test datapredictions <- predict(model, testData)# Evaluate the model with a confusion matrixconfusionMatrix(predictions, testData$Species)## Confusion Matrix and Statistics## ## Reference## Prediction setosa versicolor virginica## setosa 15 0 0## versicolor 0 14 1## virginica 0 1 14## ## Overall Statistics## ## Accuracy : 0.9556 ## 95% CI : (0.8485, 0.9946)## No Information Rate : 0.3333 ## P-Value [Acc > NIR] : < 2.2e-16 ## ## Kappa : 0.9333 ## ## Mcnemar's Test P-Value : NA ## ## Statistics by Class:## ## Class: setosa Class: versicolor Class: virginica## Sensitivity 1.0000 0.9333 0.9333## Specificity 1.0000 0.9667 0.9667## Pos Pred Value 1.0000 0.9333 0.9333## Neg Pred Value 1.0000 0.9667 0.9667## Prevalence 0.3333 0.3333 0.3333## Detection Rate 0.3333 0.3111 0.3111## Detection Prevalence 0.3333 0.3333 0.3333## Balanced Accuracy 1.0000 0.9500 0.9500
Sentiment analysis
# Load the librarieslibrary(tidytext)library(janeaustenr)library(dplyr)library(ggplot2)# Load the dataset and convert it to a tidy formatdata("austen_books")tidy_books <- austen_books() %>% unnest_tokens(word, text)# Perform sentiment analysis using the Bing lexiconsentiments <- tidy_books %>% inner_join(get_sentiments("bing")) %>% group_by(book, sentiment) %>% count()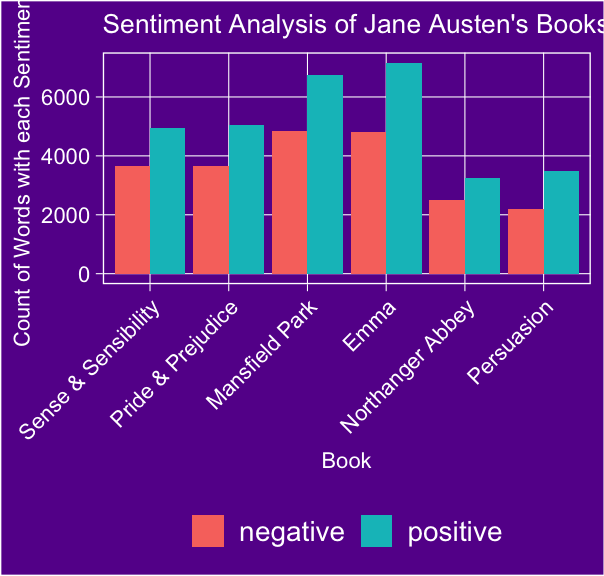
Plotting
# Load necessary librarylibrary(ggplot2)# Basic scatter plotggplot(hate_crimes, aes(x = median_house_inc, y = hate_crimes_per_100k_splc)) + geom_point() + labs(title = "Hate Crimes vs. Income", x = "Median Household Income", y = "Hate Crimes per 100k") + theme_minimal()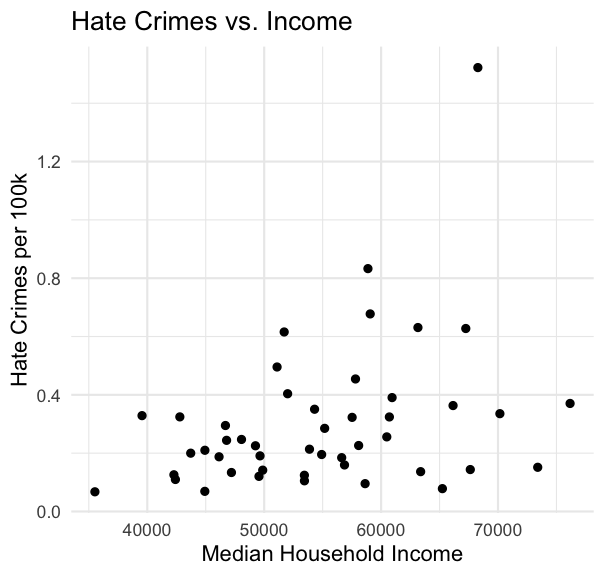
# Scatter plot with colourggplot(hate_crimes, aes(x = median_house_inc, y = hate_crimes_per_100k_splc, color = share_pop_metro)) + geom_point() + labs(title = "Hate Crimes vs.Income", x = "Median Household Income", y = "Hate Crimes per 100k", color = "Population Share (Metro)") + theme_minimal() + scale_color_gradient(low = "#FFCC33", high = "#660099")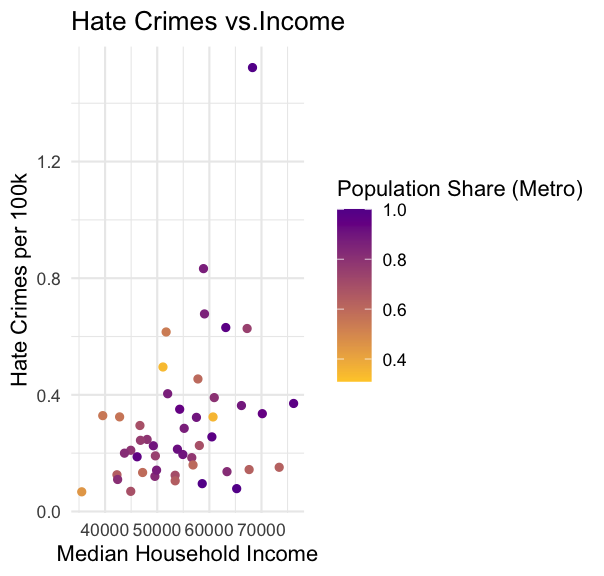
# Scatter plot with regression lineggplot(hate_crimes, aes(x = median_house_inc, y = hate_crimes_per_100k_splc, color = share_pop_metro)) + geom_point() + geom_smooth(method = "lm", se = FALSE, color = "black") + labs(title = "Hate Crimes vs.Income", x = "Median Household Income", y = "Hate Crimes per 100k", color = "Population Share (Metro)") + theme_minimal() + scale_color_gradient(low = "#FFCC33", high = "#660099")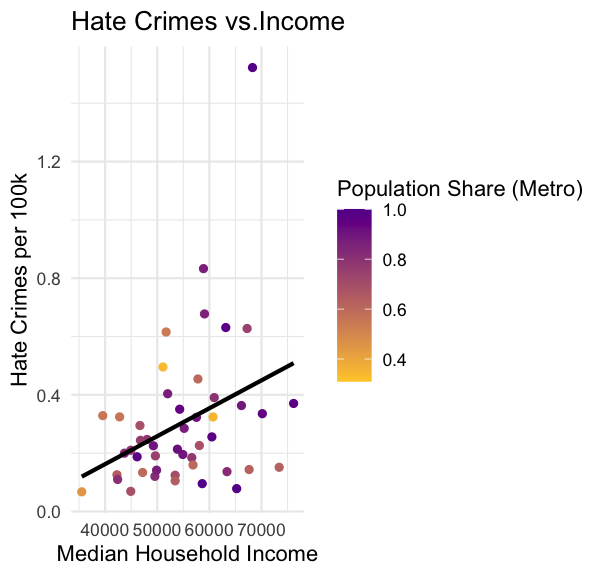
# add facetingggplot(hate_crimes, aes(x = median_house_inc, y = hate_crimes_per_100k_splc, color = share_pop_metro)) + geom_point() + geom_smooth(method = "lm", se = FALSE, color = "black") + labs(title = "The importance of Trump Voters", x = "Median Household Income", y = "Hate Crimes per 100k", color = "Population") + theme_minimal() + scale_color_gradient(low = "#FFCC33", high = "#660099") + facet_wrap(~ cut(share_vote_trump, breaks = c(-Inf, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1), labels = c("Low", "Medium", "High", "Very High")), labeller = label_both)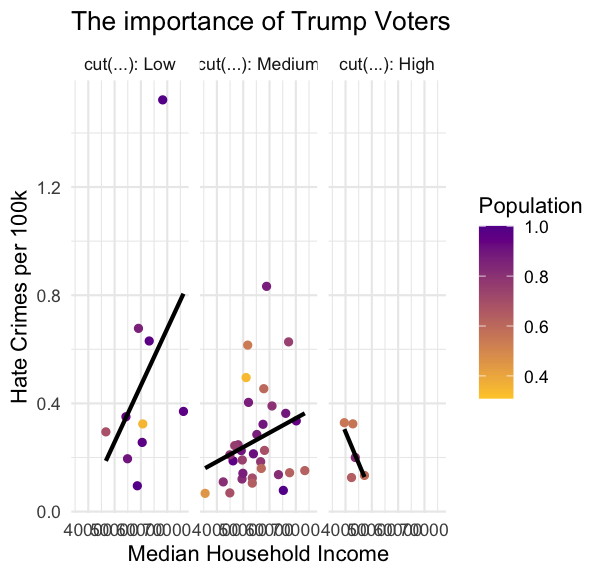
mean_hc <- mean(hate_crimes$hate_crimes_per_100k_splc, na.rm = TRUE)mean_inc <- mean(hate_crimes$median_house_inc, na.rm = TRUE)ggplot(hate_crimes, aes(x = median_house_inc, y = hate_crimes_per_100k_splc, color = share_pop_metro)) + geom_point(size = 3, alpha = 0.6) + geom_smooth(method = "lm", se = FALSE, color = "black", linetype = "dashed") + labs(title = "Hate Crimes vs. Income", x = "Median Household Income", y = "Hate Crimes per 100k", color = "Population Share (Metro)") + theme_minimal() + scale_color_gradient(low = "#FFCC33", high = "#660099") + theme(plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5, size = 14), axis.title = element_text(size = 12), legend.position = "bottom") + geom_hline(yintercept = mean_hc, linetype = "dotted", color = "grey") + geom_vline(xintercept = mean_inc, linetype = "dotted", color = "grey")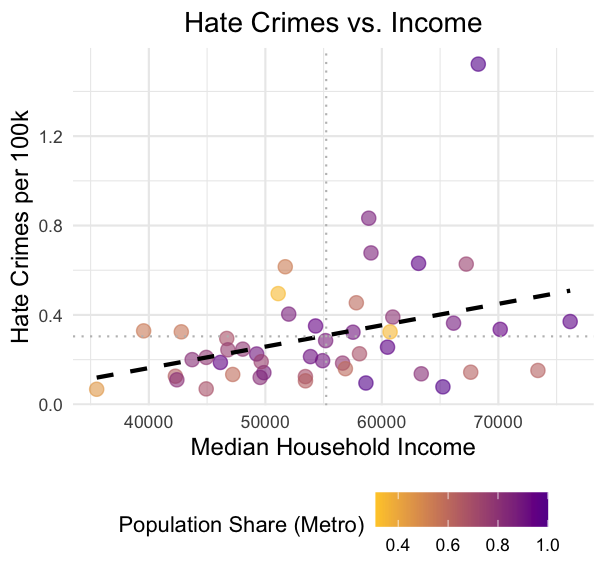
Reason 3: Reproducibility
For open science
For open science
- Enhances Transparency: Open science promotes transparency in research methods and data, allowing for better scrutiny and validation of findings.
For open science
Enhances Transparency: Open science promotes transparency in research methods and data, allowing for better scrutiny and validation of findings.
Fosters Collaboration: Sharing data and methodologies encourages collaboration among criminologists, leading to more comprehensive studies.
For open science
Enhances Transparency: Open science promotes transparency in research methods and data, allowing for better scrutiny and validation of findings.
Fosters Collaboration: Sharing data and methodologies encourages collaboration among criminologists, leading to more comprehensive studies.
Accelerates Innovation: Open access to research can accelerate the development of new theories and approaches in criminology.
For open science
Enhances Transparency: Open science promotes transparency in research methods and data, allowing for better scrutiny and validation of findings.
Fosters Collaboration: Sharing data and methodologies encourages collaboration among criminologists, leading to more comprehensive studies.
Accelerates Innovation: Open access to research can accelerate the development of new theories and approaches in criminology.
Key Resources
- CrimRxiv: An open-access preprint repository for the criminology community: https://www.crimrxiv.com/
- Open Science Working Group at the ESC:https://esc-enoc.github.io/
For yourself (e.g., changes for reviewer or repeat analysis/batch processing)
# Scatter plot with regression lineggplot(hate_crimes, aes(x = median_house_inc, y = hate_crimes_per_100k_splc, color = share_pop_metro)) + geom_point() + geom_smooth(method = "lm", se = FALSE, color = "black") + labs(title = "Hate Crimes vs.Income", x = "Median Household Income", y = "Hate Crimes per 100k", color = "Population Share (Metro)") + theme_minimal() + scale_color_gradient(low = "grey90", high = "black")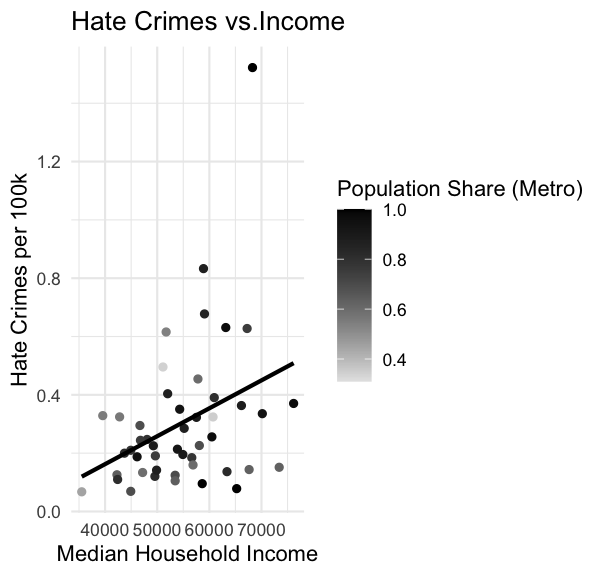
Less point and click = more transparency, less space for errors
- In 2010, economists Carmen Reinhart and Kenneth Rogoff published a paper titled "Growth in a Time of Debt."
- The paper claimed that countries with debt levels above 90% of GDP experienced slower economic growth.
- A spreadsheet error in their data analysis led to faulty conclusions.
- The findings influenced austerity measures globally, including in the EU and the US.
- Policymakers used the conclusions to justify harsh budget cuts and economic policies.
- See: https://www.bbc.com/news/magazine-22223190
Beyond analysis...
Beyond analysis...
- Slides/ reporting (demo next)
Beyond analysis...
- Slides/ reporting (demo next)
- Websites
Beyond analysis...
- Slides/ reporting (demo next)
- Websites
- Books
Is it R?

Is it R?

- these slides?
Getting Started with R
- R for Data Science: A free online book that’s an excellent resource for learning R and data science workflows.
- Hands-On Programming with R: Friendly intro to R language for non-programmers
- DataCamp: Introduction to R: Free course offering an interactive way to learn R basics.
Visualisation
- Data Visualization: A practical introduction: Beautiful book on data visualisation
- ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis: A resource for those interested to understand the logic of the Grammar of Graphics that ggplot2 uses.
R Resources for Criminology/ Social Science
- Quantitative Social Science: An Introduction: My favourite social science stats textbook - also uses R
- Discovering Statistics Using R: Very comprehensive, from field of psychology
- A Beginner’s Guide to Statistics for Criminology and Criminal Justice Using R: Written as a companion to classic stats book by Weisburd and Britt
- R for Criminologists: Our course material for PGT
- R for Criminologists: Our course material for UG
Additional Learning
- Stack Overflow: Get help from the R community by browsing or asking questions.
- R Bloggers: Collection of blogs about using R in a variety of disciplines, including criminology.
- Twitter (or maybe Blue Sky now? I don't know!!!)
Demo
Exercise
Code to copy:
# Install necessary packages if they are not already installedif(!require(ggplot2)) install.packages("ggplot2", dependencies = TRUE)if(!require(fivethirtyeight)) install.packages("fivethirtyeight", dependencies = TRUE)# Load the packageslibrary(ggplot2)library(fivethirtyeight)# Create a basic scatter plot of median_house_inc vs. hate_crimes_per_100k_splcggplot(hate_crimes, aes(x = median_house_inc, y = hate_crimes_per_100k_splc)) + geom_point(color = "blue", size = 3, alpha = 0.6) + # Scatter plot with blue points labs(title = "Hate Crimes per 100k vs. Median Household Income", x = "Median Household Income", y = "Hate Crimes per 100k") + theme_minimal() # Apply minimal theme for a clean lookExercise 1: Change the Aesthetics
- Task: Modify the color, size, or transparency of the points in the scatter plot.
- Hint: Use color, size, and alpha arguments in geom_point().
Exercise 1: Change the Aesthetics
- Task: Modify the color, size, or transparency of the points in the scatter plot.
- Hint: Use color, size, and alpha arguments in geom_point().
Answer:
# Modify color and size of pointsggplot(hate_crimes, aes(x = median_house_inc, y = hate_crimes_per_100k_splc)) + geom_point(color = "red", size = 5, alpha = 0.8) + labs(title = "Modified Scatter Plot", x = "Median Household Income", y = "Hate Crimes per 100k") + theme_minimal()Exercise 2: Add a Regression Line
- Task: Add a linear regression line to the scatter plot to show the trend.
- Hint: Use geom_smooth() with method = "lm" to add a linear model.
Exercise 2: Add a Regression Line
- Task: Add a linear regression line to the scatter plot to show the trend.
- Hint: Use geom_smooth() with method = "lm" to add a linear model.
Answer:
# Scatter plot with a regression lineggplot(hate_crimes, aes(x = median_house_inc, y = hate_crimes_per_100k_splc)) + geom_point(color = "blue", size = 3, alpha = 0.6) + geom_smooth(method = "lm", color = "black", se = FALSE) + labs(title = "Scatter Plot with Regression Line", x = "Median Household Income", y = "Hate Crimes per 100k") + theme_minimal()Exercise 3: Group Points by a Third Variable
- Task: Color the points by a third variable such as share_pop_metro to explore how urban/rural distribution affects the relationship.
- Hint: Use color = share_pop_metro inside the aes() function.
Exercise 3: Group Points by a Third Variable
- Task: Color the points by a third variable such as share_pop_metro to explore how urban/rural distribution affects the relationship.
- Hint: Use color = share_pop_metro inside the aes() function.
Answer:
# Scatter plot with points colored by share_pop_metroggplot(hate_crimes, aes(x = median_house_inc, y = hate_crimes_per_100k_splc, color = share_pop_metro)) + geom_point(size = 3, alpha = 0.6) + labs(title = "Scatter Plot by Population", x = "Median Household Income", y = "Hate Crimes per 100k", color = "Share Pop Metro") + theme_minimal() + scale_color_gradient(low = "blue", high = "red")Exercise 4: Customize the Plot Theme
- Task: Explore different ggplot2 themes such as theme_classic(), theme_bw(), or even modify axis titles, labels, and legend positions.
- Hint: Use theme() to customize the plot or apply pre-built themes like theme_classic().
Exercise 4: Customize the Plot Theme
- Task: Explore different ggplot2 themes such as theme_classic(), theme_bw(), or even modify axis titles, labels, and legend positions.
- Hint: Use theme() to customize the plot or apply pre-built themes like theme_classic().
Answer:
# Custom theme applied to scatter plotggplot(hate_crimes, aes(x = median_house_inc, y = hate_crimes_per_100k_splc, color = share_pop_metro)) + geom_point(size = 3, alpha = 0.6) + labs(title = "Scatter Plot with Custom Theme", x = "Median Household Income", y = "Hate Crimes per 100k", color = "Share Pop Metro") + theme_classic() + theme(plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5, size = 14), axis.title = element_text(size = 12), legend.position = "bottom")Thank you
Contact: reka.solymosi@manchester.ac.uk